Executive summary
The size of the Indian
consumer market is poised to reach $ 4 trillion by 2025.
It could be seen that
population drawing income between INR 500,000 and INR 20,00,0000 (i.e. Aspirers
and Affluent, in the above classification) is growing at faster rate than any
other segment in the above analysis. Together they are expected to make up 45%
of the total consumption expenditure in India in 2025. (Boston Consulting Group 2017) This strong domestic
consumer base is the strength of the Indian economy. This strong consumer base
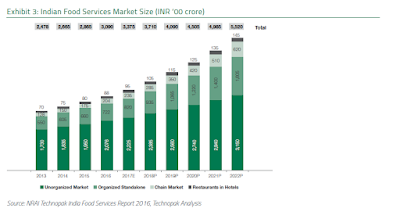
is what makes India a favorite destination for FDI. Indian Food Services market
in India (organized and unorganized) is estimated at INR 3,37,500 crore in 2017
and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10% over the next 5 years to reach INR
5,52,000 crore by 2022. (Technopak 2017)
Over the years the market
size of the restaurant chains in the food industry has been growing.
Year
|
2013
|
2014
|
2015
|
2016
|
2017
|
Market size
|
128
|
150
|
175
|
204
|
235
|
(Rs. In ‘00 Crores)
|
|||||
CAGR
(Computed)
|
17.18%
|
16.67%
|
16.57%
|
15.19%
|
As it can be seen, the
market for the restaurant chains has grown at a steady rate. Therefore, the
sector as a whole is promising in terms of consumer demand.
However the supply side
economics should also be considered. Given the unpredictability of daily
demand, there is always the risk of wastage of production on daily basis. On
the other hand, not meeting the consumer demand would impinge badly in the
minds of the customers. Hence, it is crucial to strike a balance between excess
production and short production.
Much of the solution to this
problem lies in garnering a reliable consumer base. A regular and predictable
demand for the food would help the firms to produce enough to meet the
requirement.
This reliable demand base,
in turn could be formed, only through offering food at cost effective rates.
The highest share of consumption expenditure in Indian market comes from
people, whose annual income is between INR 150,000 and INR 500,000. They alone
account for 38% of the total consumption expenditure in India as at 2016.
If the sector could come up
with innovative cost effective business models that could cater to the later
consumer segment, the prospects for this sector is very bright.
1. Sector size, Composition and
Constituents
Major Players
b)
McDonald's
The following factors affect the growth of the
restaurant industry
a)
Increasing varieties
The ever increasing culinary
recipes make dining an important experience of respite and relief.
b)
Growing mobility of restaurant services
In the recent years food delivery
service providers like Swiggy, Ubereats, Eat24 have made dining easier.
c)
Amenities
Customer’s experience at the
restaurant apart from eating influence the customer demand. More the amenities,
more the restaurant would be appealing to customers.
d)
Demographics
Almost 45% of the population is
less than 24 years. The young demographic population of the country serves as
the prime market for these restaurants.
e)
Increasing Urbanization
About 34% of India's population
now lives in urban areas, the U.N. World Urbanization Prospects 2018 report has
said. This is an increase of about three percentage points since the 2011
Census. The increasing urbanization is a promising factor for the industry to
grow as these restaurants operate in urban cities primarily.
f)
Increasing women labor
It is expected that women
employees in service sector would increase from 20% in 2011 to 25% 2020. (Technopak
2017) With more
women entering the working population, cooking at home has decreased. This in
turn has increased the demand for food at restaurants.
g)
Nuclear families
About 68% of the Indian families
are nuclear families. It is expected to grow to 75% by 2025. Nuclear families
tend to diverge from conventional practices of avoiding outside foods. With
increasing number of nuclear families, the restaurant business could see better
prospects in their way.
3. Value
chain of the sector and various business models
a) Primary activities
·
Deciding the menu for
service
·
Cooking
·
Service of the food
b) Support activities
·
Sourcing of the
ingredients
·
Dining experience
provided
·
Provision of other
amenities like TV, Lounge etc..
·
Marketing
·
Delivery services
The above classification of
primary and secondary activities has become more of a theoretical exercise,
given the competition in the industry. In order to be successful, a firm has to
provide rich experience to its customers in each of the aforesaid fronts.
4. Various
business models
5. Cost and Revenue drivers
a) Considerations for Cost
·
Cost
of the ingredient products
·
Cost
of skilled and unskilled labor
·
Rental
cost
b) Revenue drivers
·
Quality
of the food served
·
Cost
effectiveness
·
Other
Amenities offered at the restaurant
6.Risks specific to the sector
a) Skyrocketing rental costs
With the increasing real estate costs, expansion for the
restaurant chains has become a great deal.
b) Too much concentration in the metro cities
With almost all the restaurant chains focusing on capturing
the market in metro cities, there is too much strain on the markets in the
urban cities. This mutually affects the profitability of the market
participants at urban centers.
c) Risk of losing the brand value
Any action that could affect the credibility of the
restaurant at one place could affect the restaurant chain as a whole. This is
perhaps, the single most deterring risk factor that the market players need to
be wary of.
Eg: Recently central kitchen of a famous restaurant chain
was sealed for unhygienic practices by the regulators. This has led to the
restaurant chain losing competitive edge and credibility in the public arena.
7.Funding overview of the sector
|
Company
|
Debt to equity *
|
Market capitalisation**
|
Product
|
|
Westlife
development
|
0.30
|
5,477.02
|
1,643.11
|
|
Jubilant
Foodworks
|
-
|
16,409.13
|
-
|
|
Total
|
|
21,886.15
|
1,643.11
|
|
Net Debt to Equity Ratio
|
|
|
0.08
|
*Debt to equity ratio is derived from the 2nd quarter financial results of the companies for the FY 2018-19.
**Market capitalization is in Crores as at 09th
December 2018.
Westlife
development and Jubilant Foodworks, who are considered to be representative of the sector, have been
taken as proxies for the computation of the debt to equity ratio. As it can be
seen, the sector is least funded by debt and is operating primarily on its own
capital.
8.Key
performance metrics at firm level and sector level
Firm level
·
Number of
customers visits per day
·
Average
revenue per customer
·
Number
of repeat visits of a customer per year
Sector level
·
Number
of new restaurants opened in the country during a particular period
·
Contribution
of the sector to the national GDP
·
Revenue
growth of the sector Y-o-Y and Q-o-Q
8. Summary
of industry level financial performance
The chain
market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 21% to reach INR 62,000 crore by 2022
from INR 23,500 crore in 2017.The market size was at the tune of INR 20400
Crores as at 2016 and the projected market size for 2018 was INR 28,500 Crores.
9. List of
key players in the sector